Prototype building
Demo Installation
A demo installation for the large scale production of the new, aerogel-based insulation materials will be implemented in Bilzen, Belgium. An area of 1,300 m² is available for this demo plant. The following input (waste) streams will be incorporated in the aerogel production process and upgraded to high value insulation materials:
- Recycled cellulose fibres (e.g. from recycled newspaper or other industrial waste streams).
- Recycled mineral fibres (e.g. glass wool and stone wool fibres): mineral fibres within construction and demolition waste are considered largely unrecyclable. These streams can be integrated directly within the aerogel composite insulation material.
- Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam is used extensively throughout Europe as an insulation material. Currently, the amount of EPS construction waste equals 200 kton per year in Europe and may reach up to 1,000 kton per year in the decades to come. These recycled EPS streams can be used as input material to produce high thermal performant aerogel-incorporated EPS composite beads.
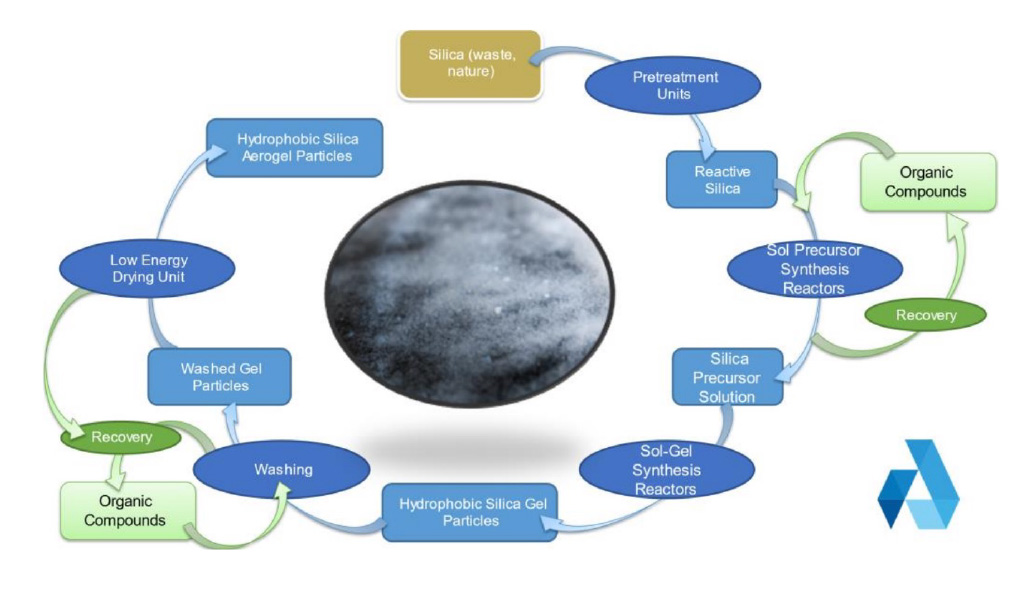
Further, local sources, including sand and plant stems will be used as raw materials for the aerogel synthesis. The process flow of the new aerogel production process is depicted in Figure 1 below.
By the end of this project, the goal is to have an operational demo plant comprising in total three reactors of 2500 litres, such that a continuous production line of three reactors in series can be installed to produce gel, which then continuously gets solvent exchanged and dried into 600 ton aerogel per year. To meet this production capacity, the line of three reactors in series will convert about 16 kg of pre-treated silica (e.g. sand) per hour into precursor material, which in turn will be diluted to a sol as output at a volumetric rate of 140 L per hour. This 140 L sol gets then converted into gel particles, which in turn are solvent exchanged and dried in a continuous fashion. During drying, the pore liquid gets continuously extracted and reused to produce new sols. This can result in the production of up to 6,000 m3 aerogel particles per year, and up to 36,000 m3 composite aerogel-based insulation material per year when mixed with recycled fibres and EPS (considering 17 vol% aerogel and 83 vol% recycled fibres or PS).
Related articles
CarbIP Life Project Newsletter – Issue 5 January 2025
Halfway there! Our approach to creating circular buildings The impact…
VLAIO Living Lab Circulair Beton
The Clusterevent Circulair Beton, organized by VLAIO Living Lab Circulair…






